4 wholesale trends that you should keep an eye on
The demands placed on wholesalers have changed considerably in recent years due to various factors. Economic challenges in particular have had a significant impact on wholesale, with logistics processing in the warehouse standing out as a particularly affected area. With a total turnover of 1.39 trillion euros in Germany and a turnover of 190.43 billion euros in Austria in 2022, wholesale is considered one of the most important pillars of economic activity in the DACH region. In view of these sales figures and the high relevance of wholesale for the economy, it is important to observe the various trends and implement them in logistics.
After all, the heart of wholesale beats in the warehouse.

These 4 trends await you
01 | From paper to pixels: How digital solutions are revolutionizing warehouse management
The wholesale warehouse is the beating heart of the customer journey. The increasing diversity of customer demands requires a flexible response to new market conditions. In order to optimize the value chain in the wholesale warehouse, it is no longer sufficient to rely on paper forms that have to be filled out manually. There is an urgent need to switch to digital solutions that enable automated data capture and management.
Here are some examples of how orders can be processed quickly and agilely in the warehouse:
Order picking
Following the introduction of guided picking systems such as Pick-by-Light, Pick-by-Voice or Pick-by-Vision, the next evolutionary step in the warehouse is the use of robots that take over all or part of the order processing tasks. This includes the collection or removal of goods, their transportation in the warehouse as well as their preparation and dispatch.
There are different types of robotic systems for automated order picking, which can be selected depending on the requirements and characteristics of the warehouse. The most common are:
- Systems based on the “goods-to-man” principle: In these systems, the products are automatically transported to the picking stations, where the employees pick and pack the desired items. The products can be stored in bins, cartons or pallets that are moved by storage and retrieval machines, conveyor belts, shuttle systems or other means of transportation. These systems are suitable for a large number of different products with low to medium demand.
- Systems based on the “man-to-goods” principle: In these systems, employees are accompanied by driverless transport vehicles or robots that offer them the products or transport the picked goods away. The products can be stored in shelves, drawers or boxes that are opened or closed by the robots. These systems are suitable for a small number of different products with high demand.
- Systems based on the “robot-to-goods” principle: In these systems, the robots take over the entire picking process by removing the products from the storage positions and bringing them to the packing stations. The products can be stored in shelves, containers or pallets, which are gripped or lifted by the robots. These systems are suitable for a large number of different products with low to high demand.
Intelligent packaging
In today's business world, intelligent packaging is essential for inventory management. Innovative packaging solutions offer a variety of benefits that are particularly useful for wholesale warehouses. Depending on the specific requirements and circumstances of a warehouse, a variety of technologies can be used. These technologies offer different benefits that optimize warehouse operations depending on individual needs:
- RFID tags: RFID tags are small devices that are used to identify and track objects using radio waves. The abbreviation RFID stands for “Radio Frequency Identification”. An RFID tag consists of a chip and an antenna; the chip stores information about the object to which the tag is attached and the antenna enables communication with an RFID reader. RFID is suitable for warehouse environments such as distribution centers, manufacturing and retail warehouses, and cold and frozen storage. The technology offers improved traceability of goods, more efficient workflows and reduced manual intervention. It enables seamless traceability from incoming to outgoing goods, optimizes inventory management and minimizes the risk of stock-outs and theft.
- Sensors: Continuous monitoring of temperature and humidity using sensors in storage and production environments, including chilled and frozen storage facilities, optimizes freshness monitoring and ensures optimal storage conditions. Functions such as material flow monitoring, temperature monitoring and unauthorized movement detection are used. Immediate warnings in the event of deviations from defined parameters enable quick quality assurance measures and reduce the risk of rejects. Sensors also support precise tracking and identification along the supply chain, simplify recalls and promote rapid responses to quality problems.
- Barcodes and QR codes: Scanning barcodes or QR codes in warehouse, product identification and retail storage applications enables quick access to key information such as storage location, product information and inventory quantities, significantly improving warehouse management efficiency. This quick accessibility speeds up workflows and significantly optimizes warehouse efficiency. In addition, barcodes and QR codes provide important information about products, such as storage instructions or expiration dates.
02 | How wholesalers are adapting to the needs of online retail and mastering the art of returns management
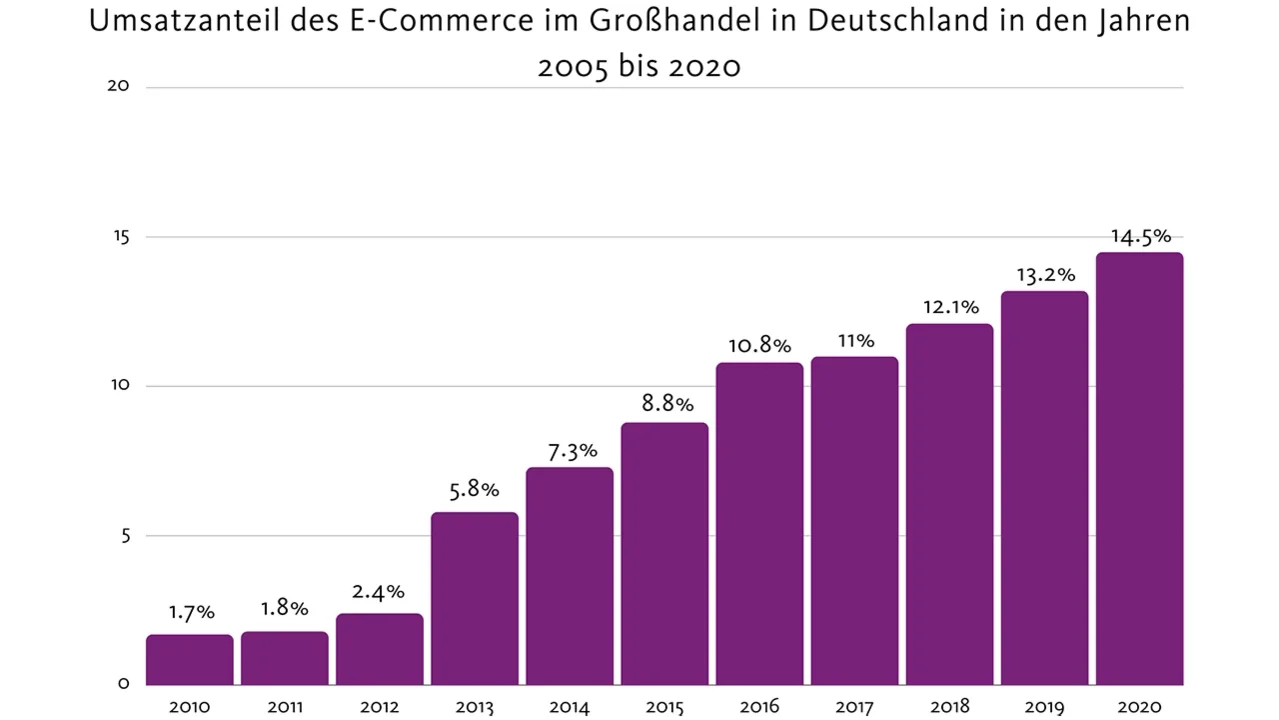
Online retail has had a significant impact on wholesale logistics processes in recent years. In 2010, sales generated online in Germany amounted to just 1.7%, whereas this has already risen to 14.5% in 2020.
This change can be attributed in part to the increase in direct sales to consumers, also known as direct-to-customer. This approach poses new challenges for wholesale logistics.
Smaller order quantities
Inventory segmentation plays a crucial role, especially for wholesale companies that sell directly to consumers and therefore have to deal with smaller order quantities. Through this segmentation, resources can be optimally utilized, shorter picking routes can be evaluated and a higher inventory turnover rate can be achieved. Inventory segmentation includes various approaches to efficiently organize and manage goods. The most common methods include
- Demand-based segmentation: This method involves categorizing products based on their demand. Products are categorized according to their demand category, such as high, medium or low demand. High demand items should be placed in areas that are easily accessible to ensure efficient access and to meet customer demand in a timely manner.
- Product-based segmentation: In this type of segmentation, products are categorized according to their type or category. Each product category, be it electronics, clothing or food, is given its own area in the warehouse. This not only makes organization easier, but also enables goods to be placed and handled in a more targeted manner.
- Customer-based segmentation: Here, products are segmented based on customer type. This can include retail customers, wholesale customers or online customers. Through this segmentation, goods can be provided according to the specific requirements and needs of the different customer groups, enabling targeted supply.
More returns
As end consumers have the right to return goods, wholesalers often have to process a large number of returns efficiently. Optimal handling of returns is critical to ensure customer satisfaction, minimize costs and keep warehouse operations running smoothly. Below you will find proven strategies and best practices to help you optimize your returns management:
- Automated returns capture: Cameras play a crucial role in managing returns by helping to capture returned items efficiently. Implementing an automated capture system makes a significant difference here. The use of cameras and automated systems speeds up the process and minimizes errors by automatically capturing information such as labels on returned products and feeding it into the system. The advantages of cameras are obvious: they enable fast and precise recording of returned items, making manual input or time-consuming processes a thing of the past.
- Sorting and classification of returned products: By using image recognition algorithms, unused items are quickly recognized and identified. The software analyzes images of the returned items and checks the condition of the goods, for example. This speeds up the process and reduces the need for manual checks. For damaged items, technological solutions help to assess the damage and decide on the next steps. Information such as the degree of damage and repair options is recorded automatically, providing warehouse employees with a sound basis for decision-making. In the case of faulty items, automated classification facilitates the return process and reduces the number of returns.
03 | From the warehouse to the customer: AI in wholesale improves processes and increases satisfaction
The use of artificial intelligence (AI) is a key trend that is fundamentally changing the wholesale sector. Through the targeted use of AI, wholesalers can not only reduce costs, but also improve the quality of their services and thus increase their competitiveness. AI is therefore becoming a decisive success factor for the future of wholesalers, as this new technology leads to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
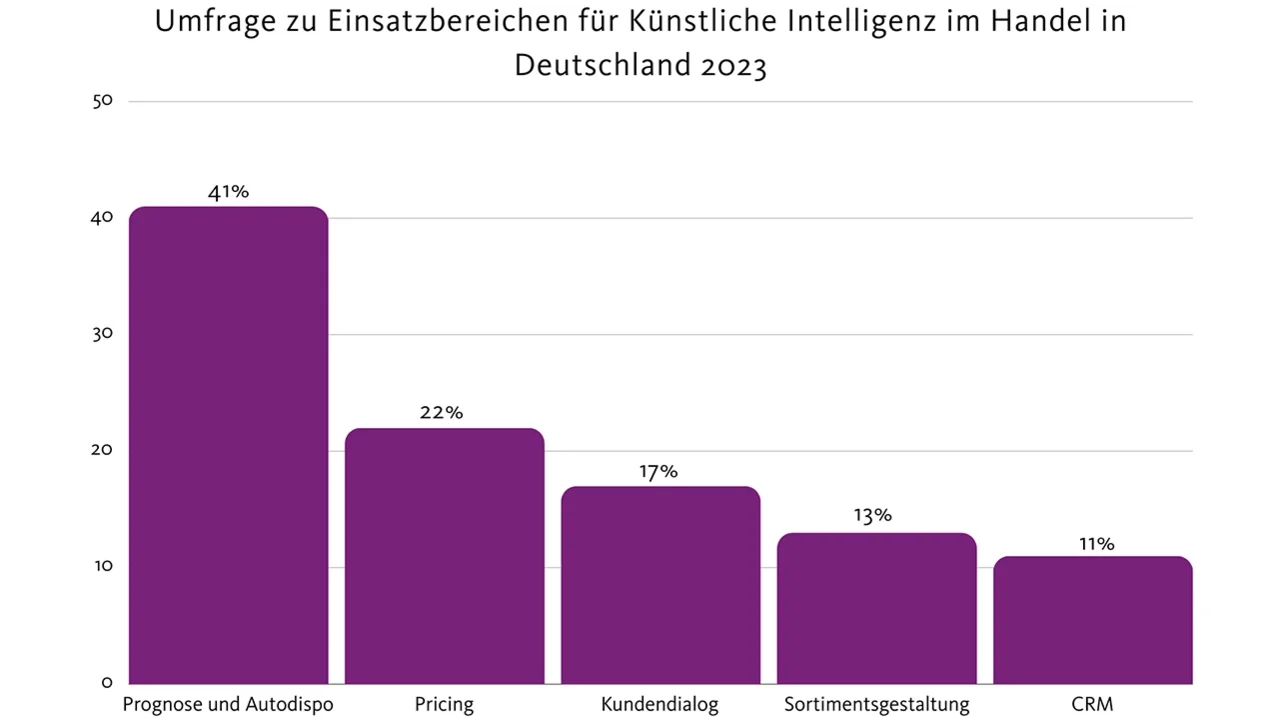
The impact of AI on the economy is undeniable and can already be clearly felt today. According to a study from 2023, 41% of German retailers are already using AI for forecasting and auto-disposition, while 22% are using this technology for pricing. It is therefore foreseeable that companies that implement AI in their processes will gain an unbeatable competitive advantage.
AI can have a significant impact in the warehouse department in particular, as time-consuming, error-prone and labor-intensive processes often take place here. Among other things, artificial intelligence offers the opportunity to revolutionize the following warehouse processes through targeted optimizations:
- Inventory management: Artificial intelligence analyzes market trends, historical data and external factors such as seasonal trends and holidays to accurately predict demand for products. On this basis, it optimizes companies' ordering strategies by precisely adjusting the quantity and timing of orders. This avoids overstocking and minimizes supply bottlenecks. In addition, the AI identifies the optimum time for orders to avoid bottlenecks in the supply chain.
- Efficient transportation and loading: Artificial intelligence helps to calculate the optimal choice of space in different storage units. Time and costs are saved not only through greater efficiency in the entire shipping process, but also through precise loading of the trucks. In addition, the AI takes into account factors such as the weight, size and shape of the freight in order to make the best possible use of the available space and minimize the risk of damage to the transported goods.
- Yard management: AI also plays a decisive role in the management of loading space on company premises. It not only supports simple placement in storage units, but also makes a significant contribution to the effective organization of cargo space. By supporting complex logistical challenges such as the planning of truck arrivals and the efficient allocation of parking spaces, AI prevents bottlenecks. This comprehensive functionality optimizes the entire logistics process by maximizing the use of resources and making operations smoother.
The areas of application for artificial intelligence (AI) in the warehouse are diverse and support a large number of processes. These include order picking, route planning and fleet management, quality control, warehouse monitoring and returns management and therefore make a significant contribution to increasing warehouse efficiency.
04| Acting responsibly: How wholesalers are improving their carbon footprint through energy efficiency and waste management
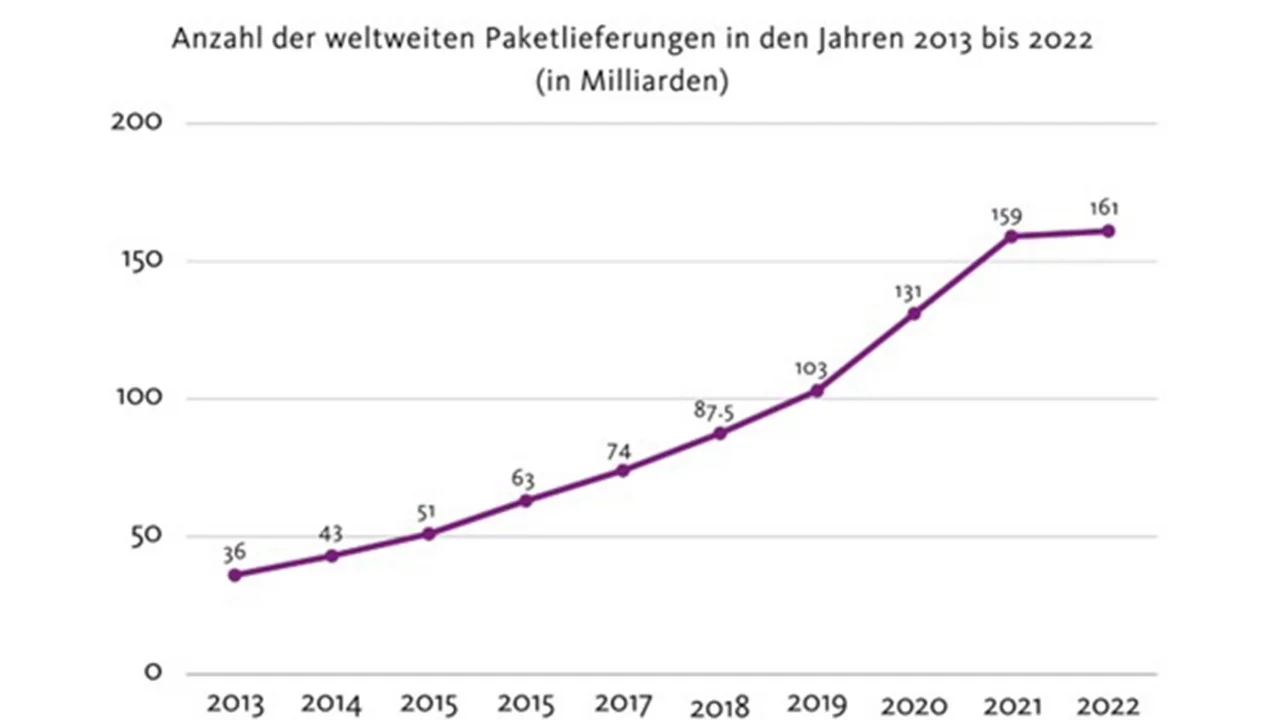
Over the last few years in particular, the wholesale sector has been influenced by rising global resource consumption and the rapid increase in parcel deliveries. The number of parcels sent has risen from 36 billion in 2013 to 161 billion in 2022.
On January 5, 2023, the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) was adopted as a new law in Europe. The aim is to increase the transparency and comparability of sustainability reporting by companies in the EU. The CSRD also requires reported information to be externally verified to confirm its accuracy, completeness and credibility. This verification must be carried out by an independent and qualified auditor in accordance with applicable standards, and the results should be summarized in an audit report and published together with the sustainability report.
The guideline is divided into three main areas: Environmental, Social and Governance. In the environmental area, companies must provide information on their impact on the environment, including climate change, biodiversity, pollution, circular economy and use of renewable energy. In the social area, reports are required on impacts on society, such as job creation, fair wages, employee health and safety, education, lifelong learning and support for local communities. The governance area includes information on corporate management, compliance with laws and standards, measures against corruption and money laundering, accountability, stakeholder participation, diversity and gender equality.
There are various ways for wholesalers to make their warehousing more sustainable:
- Energy efficiency: The use of energy-efficient equipment, lighting systems and heating and cooling technologies not only helps to reduce energy consumption and CO2 emissions, but also enables significant cost savings for companies by reducing operating costs and improving sustainability.
- Waste management: Implementing strategies to reduce, reuse and recycle packaging materials, pallets, cartons and other waste is critical to reducing companies' environmental footprint and lowering disposal costs while promoting sustainability.
- Conserving resources: Optimizing stock levels by avoiding over-ordering and extending the lifespan of products are important steps towards minimizing resource consumption. In addition, using renewable or recycled materials helps to create a more sustainable supply chain by reducing waste and lowering environmental impact.
- Social responsibility: Ensuring fair working conditions, promoting the health and safety of employees and creating an inclusive and diverse work culture are key elements of corporate responsibility. By involving the local community and creating partnerships, the company contributes to social development and increases its attractiveness as an employer, which leads to a positive image and greater employee loyalty in the long term.
Our conclusion
Wholesalers are faced with the challenging task of responding to changing customer requirements. Increasingly, digital solutions must be used. Wholesalers can only be successful in the long term by proactively adapting to technological developments. Especially in the rapidly changing retail environment, the motto is: if you don't move with the times, you'll move with the times.
This might also interest you
Invest time in building up your knowledge. This will put you in a stronger position for the future. Our webinars are also available on-demand - whatever suits you best.























































